
本系列文章md笔记(已分享)主要讨论django商城项目相关知识。项目利用Django框架开发一套前后端不分离的商城项目(4.0版本)含代码和文档。功能包括前后端不分离,方便SEO。采用Django + Jinja2模板引擎 + Vue.js实现前后端逻辑,Nginx服务器(反向代理)Nginx服务器(静态首页、商品详情页、uwsgi服务器(美多商场业务场景),后端服务:MySQL、Redis、Celery、RabbitMQ、Docker、FastDFS、Elasticsearch、Crontab,外部接口:容联云、QQ互联、支付宝。
全套笔记和代码自取在个人博客: https://www.666mao.com/sku?skuId=2
感兴趣的小伙伴可以自取哦,欢迎大家点赞转发~
共 11 章,132 子模块

用户注册业务实现
用户注册前端逻辑
为了学会使用Vue.js的双向绑定实现用户的交互和页面局部刷新效果。
1. 用户注册页面绑定Vue数据
1.准备div盒子标签
......
2.register.html
- 绑定内容:变量、事件、错误提示等
2. 用户注册JS文件实现用户交互
1.导入Vue.js库和ajax请求的库
2.准备register.js文件
绑定内容:变量、事件、错误提示等
let vm = new Vue(https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ el: '#app', // 修改Vue读取变量的语法 delimiters: ['[[', ']]'], data: https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ username: '', password: '', password2: '', mobile: '', allow: '', error_name: false, error_password: false, error_password2: false, error_mobile: false, error_allow: false, error_name_message: '', error_mobile_message: '', }, methods: https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ // 校验用户名 check_username()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ }, // 校验密码 check_password()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ }, // 校验确认密码 check_password2()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ }, // 校验手机号 check_mobile()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ }, // 校验是否勾选协议 check_allow()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ }, // 监听表单提交事件 on_submit()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ }, } });3.用户交互事件实现
methods: https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ // 校验用户名 check_username()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ let re = /^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{5,20}$/; if (re.test(this.username)) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_name = false; } else https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_name_message = '请输入5-20个字符的用户名'; this.error_name = true; } }, // 校验密码 check_password()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ let re = /^[0-9A-Za-z]{8,20}$/; if (re.test(this.password)) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_password = false; } else https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_password = true; } }, // 校验确认密码 check_password2()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ if(this.password != this.password2) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_password2 = true; } else https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_password2 = false; } }, // 校验手机号 check_mobile()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ let re = /^1[3-9]\d{9}$/; if(re.test(this.mobile)) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_mobile = false; } else https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_mobile_message = '您输入的手机号格式不正确'; this.error_mobile = true; } }, // 校验是否勾选协议 check_allow()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ if(!this.allow) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_allow = true; } else https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_allow = false; } }, // 监听表单提交事件 on_submit()https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.check_username(); this.check_password(); this.check_password2(); this.check_mobile(); this.check_allow(); if(this.error_name == true || this.error_password == true || this.error_password2 == true || this.error_mobile == true || this.error_allow == true) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ // 禁用表单的提交 window.event.returnValue = false; } }, }4. 知识要点
-
Vue绑定页面的套路
- 导入Vue.js库和ajax请求的库
- 准备div盒子标签
- 准备js文件
- html页面绑定变量、事件等
- js文件定义变量、事件等
-
错误提示
- 如果错误提示信息是固定的,可以把错误提示信息写死,再通过v-show控制是否展示
- 如果错误提示信息不是固定的,可以使用绑定的变量动态的展示错误提示信息,再通过v-show控制是否展示
-
修改Vue变量的读取语法,避免和Django模板语法冲突
- delimiters: ['[[', ']]']
-
后续的页面中如果有类似的交互和刷新效果,也可按照此套路实现
用户注册后端逻辑
1. 接收参数
提示:用户注册数据是从注册表单发送过来的,所以使用**request.POST**来提取。
username = request.POST.get('username') password = request.POST.get('password') password2 = request.POST.get('password2') mobile = request.POST.get('mobile') allow = request.POST.get('allow')2. 校验参数
前端校验过的后端也要校验,后端的校验和前端的校验是一致的
# 判断参数是否齐全 # 判断用户名是否是5-20个字符 # 判断密码是否是8-20个数字 # 判断两次密码是否一致 # 判断手机号是否合法 # 判断是否勾选用户协议
# 判断参数是否齐全 if not all([username, password, password2, mobile, allow]): return http.HttpResponseForbidden('缺少必传参数') # 判断用户名是否是5-20个字符 if not re.match(r'^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{5,20}$', username): return http.HttpResponseForbidden('请输入5-20个字符的用户名') # 判断密码是否是8-20个数字 if not re.match(r'^[0-9A-Za-z]{8,20}$', password): return http.HttpResponseForbidden('请输入8-20位的密码') # 判断两次密码是否一致 if password != password2: return http.HttpResponseForbidden('两次输入的密码不一致') # 判断手机号是否合法 if not re.match(r'^1[3-9]\d{9}$', mobile): return http.HttpResponseForbidden('请输入正确的手机号码') # 判断是否勾选用户协议 if allow != 'on': return http.HttpResponseForbidden('请勾选用户协议')提示:这里校验的参数,前端已经校验过,如果此时参数还是出错,说明该请求是非正常渠道发送的,所以直接禁止本次请求。
3. 保存注册数据
- 这里使用Django认证系统用户模型类提供的 create_user() 方法创建新的用户。
- 这里 create_user() 方法中封装了 set_password() 方法加密密码。
# 保存注册数据 try: User.objects.create_user(username=username, password=password, mobile=mobile) except DatabaseError: return render(request, 'register.html', https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{'register_errmsg': '注册失败'}) # 响应注册结果 return http.HttpResponse('注册成功,重定向到首页')如果注册失败,我们需要在页面上渲染出注册失败的提示信息。
{% if register_errmsg %} https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{{ register_errmsg }} {% endif %}4. 响应注册结果
- 重要提示:注册成功,重定向到首页
1.创建首页广告应用:contents
$ cd ~/projects/meiduo_project/meiduo_mall/meiduo_mall/apps $ python ../../manage.py startapp contents
2.定义首页广告视图:IndexView
class IndexView(View): """首页广告""" def get(self, request): """提供首页广告界面""" return render(request, 'index.html')3.配置首页广告路由:绑定命名空间
# contents url(r'^', include('contents.urls', namespace='contents')),# 首页广告 url(r'^$', views.IndexView.as_view(), name='index'),
4.测试首页广告是否可以正常访问
http://127.0.0.1:8000/
5.响应注册结果:重定向到首页
# 响应注册结果 return redirect(reverse('contents:index'))5. 知识要点
-
后端逻辑编写套路:
- 业务逻辑分析
- 接口设计和定义
- 接收和校验参数
- 实现主体业务逻辑
- 响应结果
-
注册业务逻辑核心思想:
- 保存用户注册数据
状态保持
说明:
- 如果需求是注册成功后即表示用户登入成功,那么此时可以在注册成功后实现状态保持
- 如果需求是注册成功后不表示用户登入成功,那么此时不用在注册成功后实现状态保持
美多商城的需求是:注册成功后即表示用户登入成功
1. login()方法介绍
-
用户登入本质:
- 状态保持
- 将通过认证的用户的唯一标识信息(比如:用户ID)写入到当前浏览器的 cookie 和服务端的 session 中。
-
login()方法:
- Django用户认证系统提供了login()方法。
- 封装了写入session的操作,帮助我们快速登入一个用户,并实现状态保持。
-
login()位置:
- django.contrib.auth.__init__.py文件中。
login(request, user, backend=None)
4. 状态保持 session 数据存储的位置:**Redis数据库的1号库** ```python SESSION_ENGINE = "django.contrib.sessions.backends.cache" SESSION_CACHE_ALIAS = "session"
2. login()方法登入用户
# 保存注册数据 try: user = User.objects.create_user(username=username, password=password, mobile=mobile) except DatabaseError: return render(request, 'register.html', https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{'register_errmsg': '注册失败'}) # 登入用户,实现状态保持 login(request, user) # 响应注册结果 return redirect(reverse('contents:index'))3. 查看状态保持结果
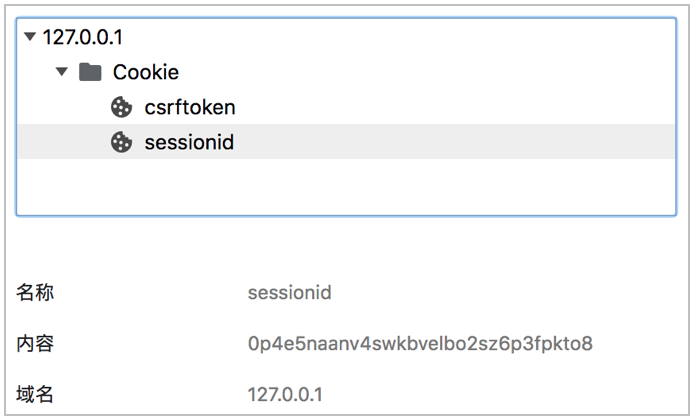

4. 知识要点
- 登入用户,并实现状态保持的方式:login(request, user, backend=None)
用户名重复注册
1. 用户名重复注册逻辑分析
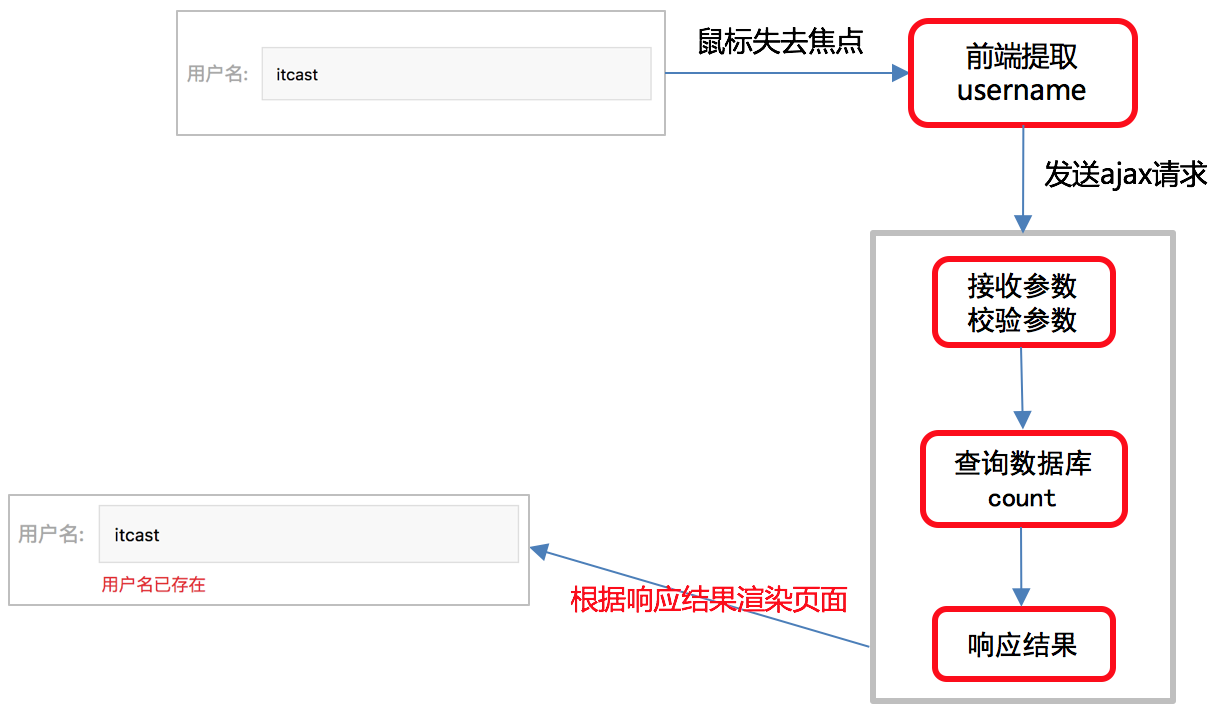
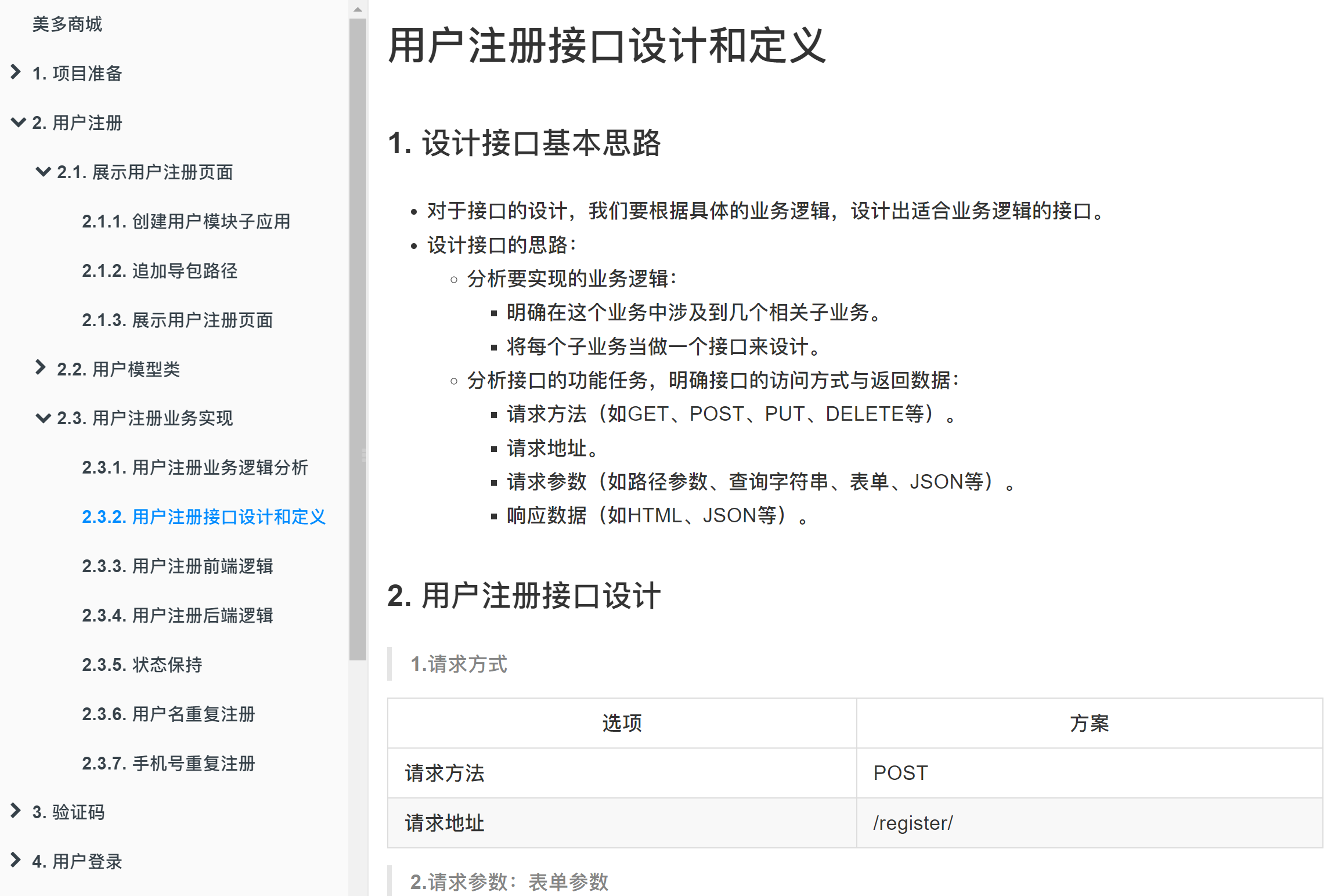
2. 用户名重复注册接口设计和定义
1.请求方式
选项 方案 请求方法 GET 请求地址 /usernames/(?P[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{5,20})/count/ 2.请求参数:路径参数
参数名 类型 是否必传 说明 username string 是 用户名 3.响应结果:JSON
响应结果 响应内容 code 状态码 errmsg 错误信息 count 记录该用户名的个数 3. 用户名重复注册后端逻辑
class UsernameCountView(View): """判断用户名是否重复注册""" def get(self, request, username): """ :param request: 请求对象 :param username: 用户名 :return: JSON """ count = User.objects.filter(username=username).count() return http.JsonResponse(https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{'code': RETCODE.OK, 'errmsg': 'OK', 'count': count})4. 用户名重复注册前端逻辑
if (this.error_name == false) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ let url = '/usernames/' + this.username + '/count/'; axios.get(url,https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ responseType: 'json' }) .then(response => https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ if (response.data.count == 1) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_name_message = '用户名已存在'; this.error_name = true; } else https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_name = false; } }) .catch(error => https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ console.log(error.response); }) }5. 知识要点
-
判断用户名重复注册的核心思想:
- 使用用户名查询该用户名对应的记录是否存在,如果存在,表示重复注册了,反之,没有重复注册。
-
axios发送异步请求套路:
- 处理用户交互
- 收集请求参数
- 准备请求地址
- 发送异步请求
- 得到服务器响应
- 控制界面展示效果
手机号重复注册
1. 手机号重复注册逻辑分析
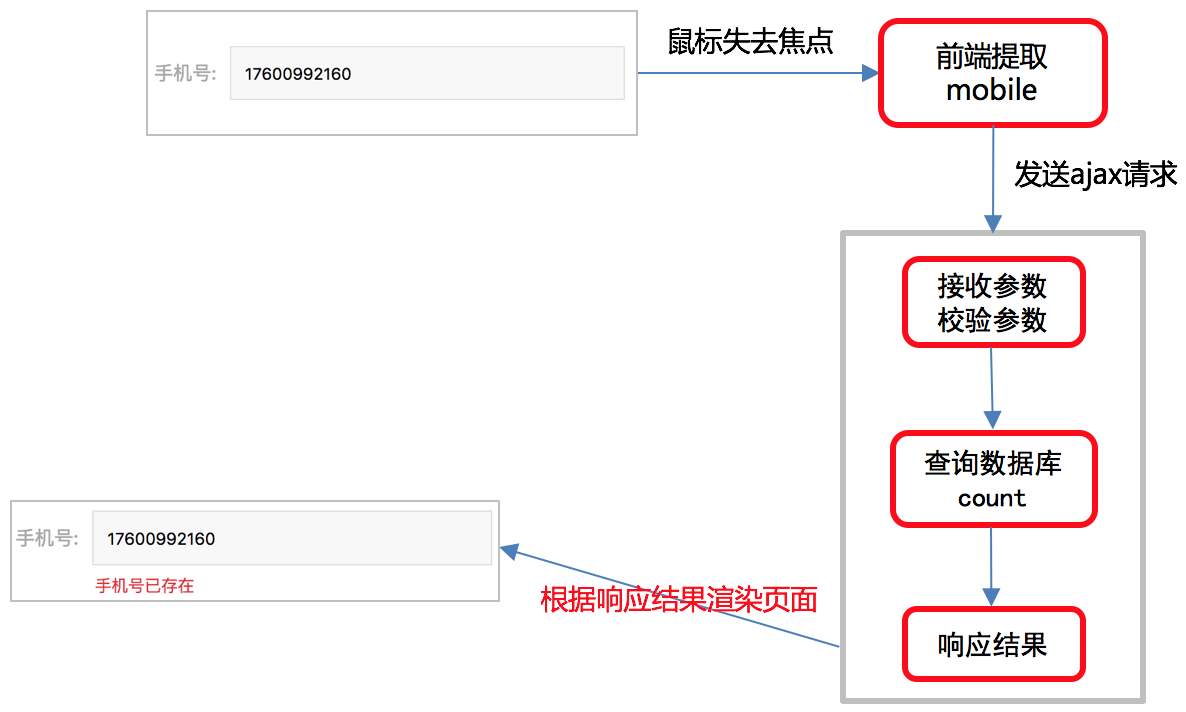
2. 手机号重复注册接口设计和定义
1.请求方式
选项 方案 请求方法 GET 请求地址 /mobiles/(?P1[3-9]\d{9})/count/ 2.请求参数:路径参数
参数名 类型 是否必传 说明 mobile string 是 手机号 3.响应结果:JSON
响应结果 响应内容 code 状态码 errmsg 错误信息 count 记录该用户名的个数 3. 手机号重复注册后端逻辑
class MobileCountView(View): """判断手机号是否重复注册""" def get(self, request, mobile): """ :param request: 请求对象 :param mobile: 手机号 :return: JSON """ count = User.objects.filter(mobile=mobile).count() return http.JsonResponse(https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{'code': RETCODE.OK, 'errmsg': 'OK', 'count': count})4. 手机号重复注册前端逻辑
if (this.error_mobile == false) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ let url = '/mobiles/'+ this.mobile + '/count/'; axios.get(url, https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ responseType: 'json' }) .then(response => https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ if (response.data.count == 1) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_mobile_message = '手机号已存在'; this.error_mobile = true; } else https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ this.error_mobile = false; } }) .catch(error => https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{ console.log(error.response); }) }验证码
图形验证码
图形验证码逻辑分析
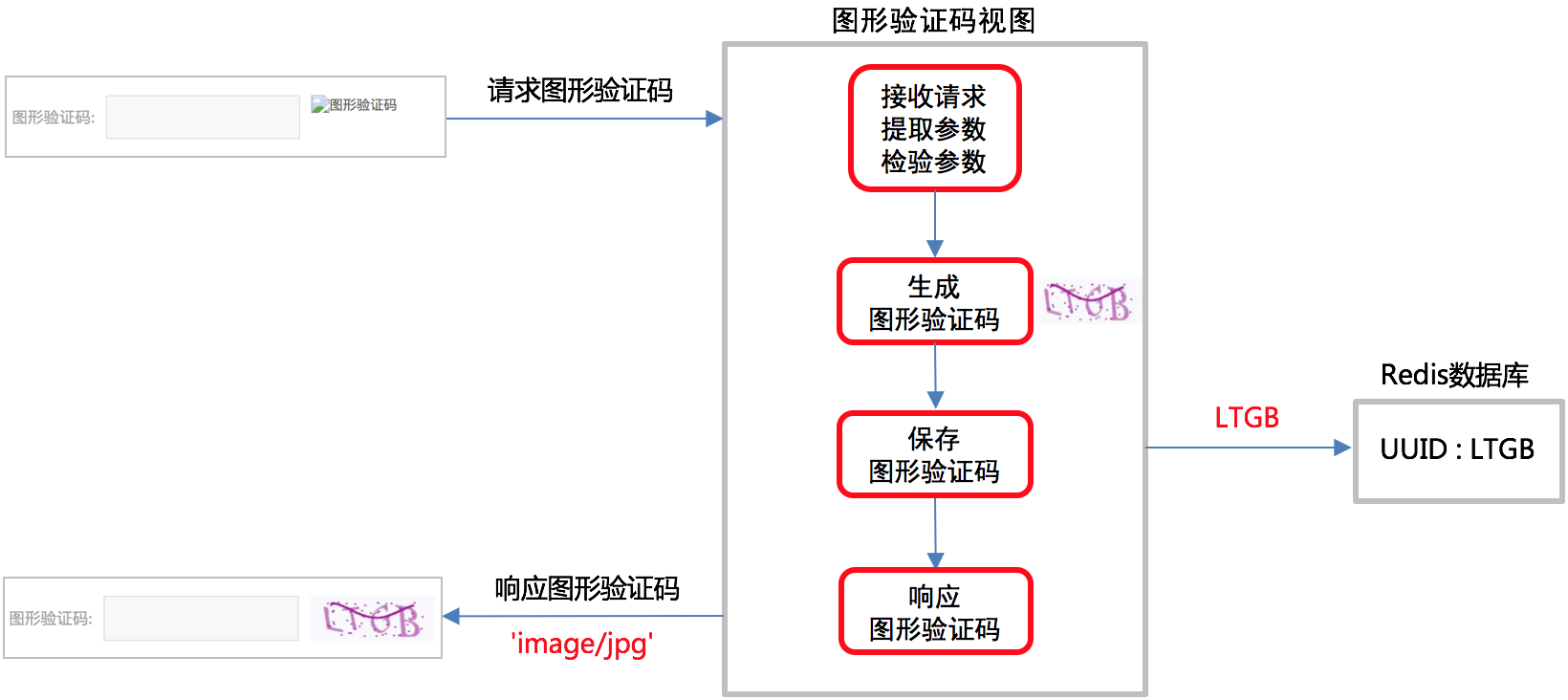
需要新建应用verifications
知识要点
- 将图形验证码的文字信息保存到Redis数据库,为短信验证码做准备。
- UUID 用于唯一区分该图形验证码属于哪个用户,也可使用其他唯一标识信息来实现。
未完待续, 同学们请等待下一期
全套笔记和代码自取在个人博客: https://www.666mao.com/sku?skuId=2
感兴趣的小伙伴可以自取哦,欢迎大家点赞转发~
r_mobile == false) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{
let url = ‘/mobiles/’+ this.mobile + ‘/count/’;
axios.get(url, https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{
responseType: ‘json’
})
.then(response => https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{
if (response.data.count == 1) https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{
this.error_mobile_message = ‘手机号已存在’;
this.error_mobile = true;
} else https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{
this.error_mobile = false;
}
})
.catch(error => https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72919230/article/details/{
console.log(error.response);
})
}
# 验证码 # 图形验证码 # 图形验证码逻辑分析 [外链图片转存中...(img-gTfk28oA-1706789118562)] > 需要新建应用`verifications` ### 知识要点 1. 将图形验证码的文字信息保存到Redis数据库,为短信验证码做准备。 2. UUID 用于唯一区分该图形验证码属于哪个用户,也可使用其他唯一标识信息来实现。 # 未完待续, 同学们请等待下一期 # 全套笔记和代码自取在个人博客: [https://www.666mao.com/sku?skuId=2](https://www.666mao.com/sku?skuId=2) # 感兴趣的小伙伴可以自取哦,欢迎大家点赞转发~
-
-
- 重要提示:注册成功,重定向到首页
-
猜你喜欢
网友评论
- 搜索
- 最新文章
- 热门文章
